선언적인 프로그래밍에 굉장히 많은 관심을 갖고 있다.
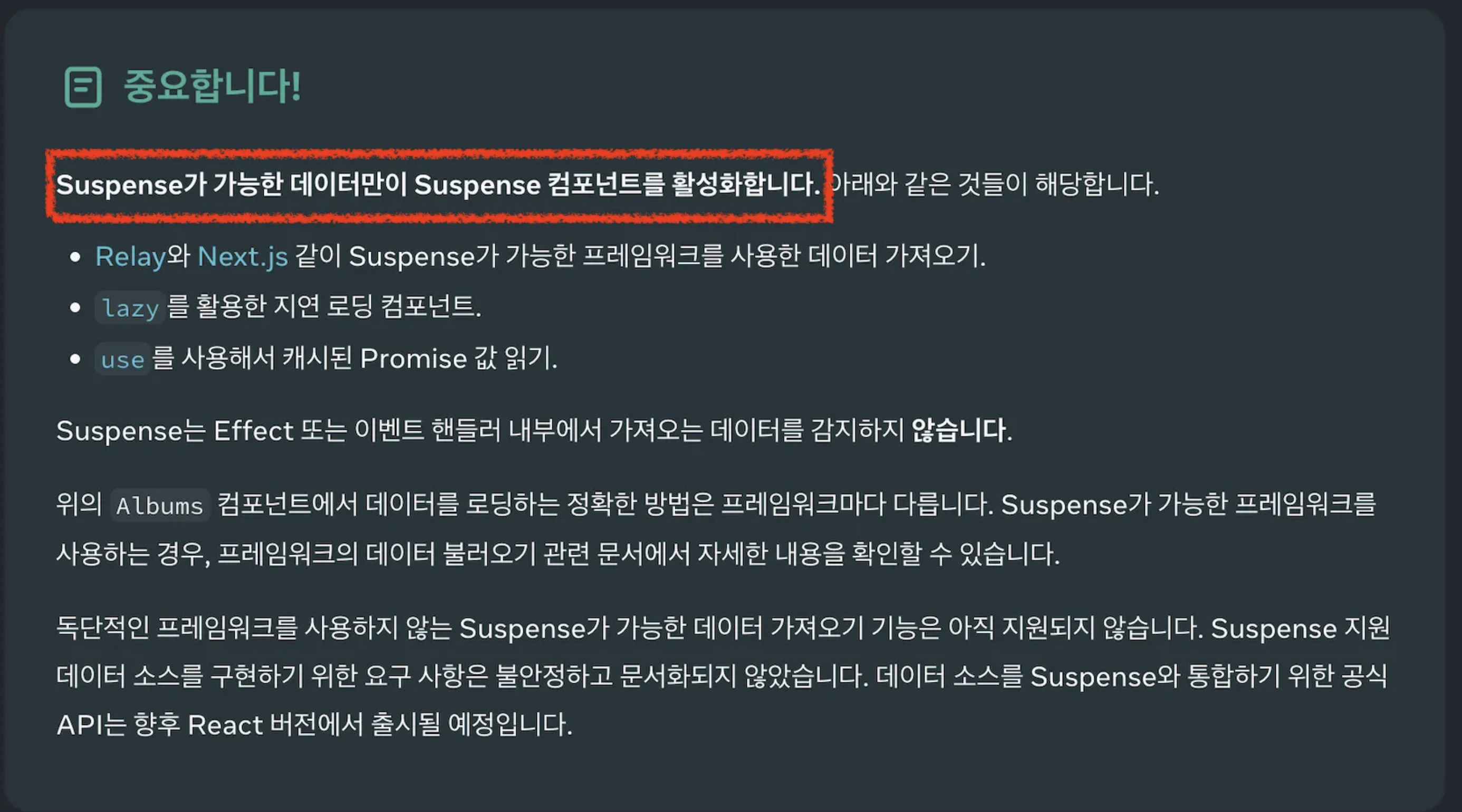
Suspense는 마법처럼 로딩 상태를 외부에 위임할 수 있다는 점때문에,굉장히 많이 사용하고 있다.
어떻게 그 기능을 구현했을까?
내가 좋아하는 기능이라면, 원리는 알고 사용하자
라는 궁금증과 마음가짐으로 React 내부 구조를 분석해보고자 한다.
기존의 React 코드
const [data, setData] = React.useState(null);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = React.useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
fetchData()
.then((result) => {
setData(result);
setIsLoading(false);
})
}, []);
if (isLoading) return <div>Loading...</div>;
return (
<div>
<h1>Data Loaded</h1>
<p>{JSON.stringify(data)}</p>
</div>
);
}
많은 관심사가 섞여있음
1. 서버 상태 로직
useEffect(() => {
fetchData()
.then((result) => {
setData(result);
setIsLoading(false);
})
}, []);
2. 렌더 로직
return (
<div>
<h1>Data Loaded</h1>
<p>{JSON.stringify(data)}</p>
</div>
);
3. 로딩 로직
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = React.useState(true);
if (isLoading) return <div>Loading...</div>;
관심사 분리가 전혀 안 되어, 디버깅이 매우 어렵다.
어디를 고쳐야 해?

명령형 프로그래밍을 선언적으로 바꿀 순 없을까?

어 왔어?? 그래그래 Dan 형이야~
Stack 아키텍처의 React 메인 컨테이너
Suspense 아이디어 창시자

마법 같은 일이 펼쳐집니다 ! (React 문서 톤으로)
Suspense 란?
- 로딩 상태를 선언적으로 처리할 수 있는 컴포넌트
function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<DataComponent />
</Suspense>
);
}
function DataComponent() {
const data = fetchData();
return (
<div>
<h1>Data Loaded</h1>
<p>{JSON.stringify(data)}</p>
</div>
);
}
AsyncBoundary
<ErrorBoundary>
<Suspense>
</Suspense>
</ErrorBoundary>우와 대박이다.
.
.
.
그래그래 대박인건 알겠는데, 어떻게 했지?
Key Idea
throw Promise를 기억해주세요.
- Promise를 던져, 평가 맥락을 바꾼다
Prerequisite
try / catch
catch는 에러만 감지하는 게 아니라, throw된 모든 것을 감지한다.
try {
throw "문자열도 던질 수 있음";
} catch (e) {
console.log("catch로 들어옴:", e);
// 출력: catch로 들어옴: 문자열도 던질 수 있음
}
Fiber
- 렌더링 과정을 세밀하게 쪼개고 관리하기 위한 내부 구조
- 동시성 처리를 위해 기존의 스택 구조에서 마이그레이션
export type Fiber = {
tag: WorkTag, // 컴포넌트 구분자
type: any,
return: Fiber | null, // 부모 Fiber
flags: Flags, // 현재 상태를 나타내는 플래그
lanes: Lanes, // 우선순위
alternate: Fiber | null // current <-> workInProgress를 가리키는 플래그
};
ReactElement
- React 내부에서 사용하는 순수한 자바스크립트 객체 (JSX 평가 결과)
- 번들러가 변환함(transpiled by webpack, esbuild)
function ReactElement(
type, // 컴포넌트 타입 (보통 함수)
key, // key
self,
source,
owner, // ReactElement를 만든 객체
props, // props
// ...
) {
// ...
const element = {
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
type,
key,
ref,
props,
};
return element;
}React 내부 동작의 Cycle
- Trigger (마운트, 업데이트)
- Scheduling (어떤 작업을 언제, 어느 우선순위로 수행할지 결정)
- Reconciliation (Fiber 트리를 만들며 무엇이 어떻게 바뀌는지 계산) 👀👀👀👀👀👀
- Commit (실제 DOM 반영)
Fiber 평가 순서
- 기본적으로 DFS (우선순위에 따라 상이)
- 현재 Fiber → 자식 Fiber → 형제 Fiber → 부모 Fiber
고생하셨습니다
이제 정말 React 내부 코드의 흐름을 따라가며, 동작을 분석해보겠다.
이 글에서는 Suspense의 재조정 단계에 대해서만 살펴볼 예정이다.
예제 코드
import { Suspense } from "react";
export default function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>loading..</div>}>
<ABC />
</Suspense>
);
}
function ABC() {
throw new Promise<void>((res) => res()); // *
return <main>ABC ! </main>;
}
- App → Suspense → ABC → div → main
- 순서대로 평가
performSyncWorkOnRoot
재조정의 엔트리 포인트
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {
// ...
let exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes); // * 시작
// ...
return null;
}renderRootSync
Fiber 트리 순회 → 각 Fiber에 대해 재조정 반복 트리거
function renderRootSync(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
// ...
do {
try {
workLoopSync();
break;
} catch (thrownValue) { // Promise !
handleError(root, thrownValue); // Promise !
}
} while (true);
// ...
}workLoopSync
(Fiber 트리를 순회하며 처리하는 루프임, performUnitOfWork만 호출하는 역할)
function workLoopSync() {
while (workInProgress !== null) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}performUnitOfWork
Fiber 하나씩 처리, beginWork → completeUnitOfWork 순
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
const current = unitOfWork.alternate;
const next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, subtreeRenderLanes); // *
if (next === null) {
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork); // *
} else {
workInProgress = next; // *
}
// ...
}beginWork
Fiber type에 따라 초기화·업데이트 실행 (거대한 switch/case 분기)
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null, // 현재 Fiber Tree
workInProgress: Fiber, // 임시 Fiber Tree
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...
didReceiveUpdate = false;
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent: { // *
return mountIndeterminateComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
workInProgress.type, // Component
renderLanes,
);
}
// ...
}mountIndeterminateComponent
- renderWithHooks 호출해 JSX 평가
function mountIndeterminateComponent(
_current,
workInProgress,
Component,
renderLanes,
) {
const props = workInProgress.pendingProps; // props 처리
const value = renderWithHooks(
null,
workInProgress,
Component,
props,
context,
renderLanes,
);
// ...
}renderWithHooks
- 컴포넌트를 실행하는 함수 (현재 컴포넌트 <ABC/>)
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
// ...
props: Props, // props
secondArg: SecondArg,
// ...
): any {
// ...
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// ...
}
function ABC() {
throw new Promise<void>((res) => res()); // *
return <main>ABC !</main>;
}
- 이때 ABC 컴포넌트 평가
- throw new Promise(...) 실행 → Promise 감지!!!
상위의 renderRootSync 의 catch 문으로 맥락이 이동한다
function renderRootSync(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
// ...
do {
try {
workLoopSync();
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleError(root, thrownValue); // Promise !
}
} while (true);
// ...
}
아래에는 이러한 핵심 내용으로 이뤄져 있다.
1. 던져진 Promise를 감지 및 핸들링
2. Suspense 컴포넌트 찾기
3. fallback 렌더링
handleError
- throw 핸들링
function handleError(root, thrownValue): void {
do {
// ...
let erroredWork = workInProgress;
throwException(
root,
erroredWork.return,
erroredWork,
thrownValue, // Promise !
workInProgressRootRenderLanes,
);
completeUnitOfWork(erroredWork);
} catch (yetAnotherThrownValue) {
// ...
} while (true);
}throwException
- 컴포넌트를 불완전한 상태로 전환
- 던져진 에러가 Promise라면(thenable), Suspense Boundary를 찾는다
function throwException(
root: FiberRoot,
returnFiber: Fiber,
sourceFiber: Fiber,
value: mixed,
rootRenderLanes: Lanes,
) {
// workInProgress를 미완료로 표시
sourceFiber.flags |= Incomplete;
// Promise가 던져졌는지 확인 (thenable)
if (
value !== null &&
typeof value === 'object' &&
typeof value.then === 'function'
) {
const wakeable: Wakeable = (value: any);
// 가장 가까운 Suspense 찾기
const suspenseBoundary = getNearestSuspenseBoundaryToCapture(returnFiber);
// Suspense Boundary가 있다면, shouldCapture flag 추가
if (suspenseBoundary !== null) {
markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture(
suspenseBoundary,
returnFiber,
sourceFiber,
root,
rootRenderLanes,
);
return; // void return으로, 다음 단계 진입
}
// ...
} while (workInProgress !== null);
}markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture
- 에러를 잡아야 한다는 표시인 ShouldCapture 플래그를 추가한다
function markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture(
suspenseBoundary: Fiber,
returnFiber: Fiber,
sourceFiber: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
rootRenderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...
// 에러를 캡처해야 한다는 것을 표시
suspenseBoundary.flags |= ShouldCapture; // *
suspenseBoundary.lanes = rootRenderLanes;
return suspenseBoundary;
}completeUnitOfWork / unwindWork
- Fiber는 ShouldCapture 상태이고 Suspense로 래핑되어 있으므로, 상위 트리로 이동하며 Suspense 컴포넌트를 찾는 단계
- unwindWork / completeUniOfWork를 반복하며, 상위 트리로 이동하며 Suspense 컴포넌트를 찾는다
completeUnitOfWork (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <ABC/>)
컴포넌트의 불완전함을 해소할 때까지, 상위 컴포넌트로 불완전함(Incomplete)를 전파한다
function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void { // workInProgress
let completedWork = unitOfWork;
do {
if ((completedWork.flags & Incomplete) === NoFlags) {
// ...
} else {
const next = unwindWork(current, completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes);// *
// returnFiber === <Suspense/>
// 현재 파이버가 불완전하다면, 불완전이 해소될 때까지 부모 컴포넌트로 전파
if (returnFiber !== null) {
returnFiber.flags |= Incomplete;
// ..
} else {
// ...
}
}
// 현재의 workInProgress를 부모 컴포넌트로 변경
completedWork = returnFiber;
workInProgress = completedWork;
} while (completedWork !== null);
// ...
}
unwindWork (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <ABC/>)
<ABC/>에 해당하는 컴포넌트가 없어 null 반환
null을 반환하면 계속 트리를 탐색해야 함을 알린다
function unwindWork(
current: Fiber | null, // current,
workInProgress: Fiber, // workInProgress
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
// ...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
// ...
default:
return null; // *
}
}
completeUniOfWork (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <Suspense/>)
function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
// ...
do {
if ((completedWork.flags & Incomplete) === NoFlags) {
// ...
} else {
// returnFiber은 <App/>
const next = unwindWork(current, completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes);
if (next !== null) {
next.flags &= HostEffectMask;
// 현재 WIP를 suspense 파이버로 설정하고 종료
workInProgress = next;
return;
};
// ...
} while (completedWork !== null);
}
unwindWork (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <Suspense/>)
Suspense 컴포넌트를 찾았으므로, 추가적인 평가를 종료하기 위해 null이 아닌 workInProgress를 return한다
function unwindWork(
current: Fiber | null, // current,
workInProgress: Fiber, // workInProgress
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
// ...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case SuspenseComponent: {
// ...
const flags = workInProgress.flags;
if (flags & ShouldCapture) {
// 감지해야함 삭제 + 감지되었음 표시
workInProgress.flags = (flags & ~ShouldCapture) | DidCapture;
return workInProgress; // null이 아닌 값을 return하며 종료
}
}
// ...
}
현재까지의 상황
- 컴포넌트 평가 중, throw된 Promise를 감지했다
- renderWithHooks -> renderRootSync -> handleError
- throw된 Promise를 처리하고자, 상위 컴포넌트로 이동하며 Suspense 컴포넌트를 찾았다
- completeUnitOfWork, unwindWork 반복하며 순회
Suspense 컴포넌트에서 ShouldCapture를 잡았으므로
상위 컴포넌트를 찾아가기 위해 반복문을 수행하지 않아도 된다.
평가 맥락은 handleError로 돌아온다
handleError (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <Suspense/>
function handleError(root, thrownValue): void {
do {
let erroredWork = workInProgress;
// ...
throwException(
root,
erroredWork.return,
erroredWork,
thrownValue,
workInProgressRootRenderLanes,
);
completeUnitOfWork(erroredWork); // 이 코드까지 실행된 상태
} catch (yetAnotherThrownValue) {}
// ...
// throw된 게 없으므로 종료
return;
} while (true);
}rederRootSync (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <Suspense/>)
Suspense 컴포넌트의 workLoopSync로 이동
function renderRootSync(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
// ...
do {
try {
workLoopSync(); // 다시 평가, 현재 컴포넌트는 Supsense
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleError(root, thrownValue);
}
} while (true);
// ...
}
다시 performUnitOfWork, beginWork를 거쳐 Suspense 컴포넌트를 평가한다
updateSuspenseComponent (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <Suspense/>)
Suspense에서 fallback을 렌더링하기 위해 Suspense 컴포넌트를 업데이트
1. primaryChildren: Suspense가 래핑한 컴포넌트
2. fallbackChildren: Suspense에 prop으로 전달한 fallback
function updateSuspenseComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes) {
// ...
let showFallback = false;
const didSuspend = (workInProgress.flags & DidCapture) !== NoFlags; // 캡처됨
if (didSuspend) {
showFallback = true;
// ...
}
// 첫 마운트 시점
if (current === null) {
// ...
const nextPrimaryChildren = nextProps.children;
const nextFallbackChildren = nextProps.fallback;
if (showFallback) {
const fallbackFragment = mountSuspenseFallbackChildren(
workInProgress,
nextPrimaryChildren,
nextFallbackChildren,
renderLanes,
);
// ...
return fallbackFragment;
// ...
}
}
}workLoopSync (현재 평가 컴포넌트 <Fallback/>
이제 다시 평가맥락은 Fallback 컴포넌트로 이동하며, 렌더링을 시도한다.
function workLoopSync() {
// workInProgress는 현재 fallback임
while (workInProgress !== null) {
// 다시 렌더링
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}
Use Case
여기서 자연스럽게 생각나는 한 가지
- 라이브러리는 이걸 어떻게 지원하는 걸까?
여러분들의 대답이 궁금해요.
- 가장 처음에 기억해달라고 요청 드렸던 것이 무엇이었죠??
정답입니다.
- 바로 Promise를 throw한다는 점이죠.
tanstack-query의 suspense query는 promise를 던져 Suspense를 트리거합니다.
export function useBaseQuery(
// ...
): QueryObserverResult<TData, TError> {
// ...
if (shouldSuspend(defaultedOptions, result)) {
throw fetchOptimistic(defaultedOptions, observer, errorResetBoundary)
}
// ...
}
느낀점
1. Promise를 던져 코드의 맥락을 catch 내부로 이동시킨다는 점이 굉장히 흥미롭다.
2. 그래프 자료구조를 사용해, 자바스크립트로 UI를 계산하고 처리하는 점
3. React 수준의 라이브러리를 분석하는 것은 많은 에너지와 시간이 소요되지만, 끝까지 포기하지 않으면 수확이 존재한다.
4. React의 lazy, Next의 dynamic 내부에서도 Promise를 던질 것이라고 예측할 수 있다.
여담
React를 코드를 분석하다가 주석을 보고 기여를 시도했는데, 아직 답변이 없으심 ㅜ
fix: remove mountWorkInProgressOffscreenFiber function by Collection50 · Pull Request #31473 · facebook/react
Summary I deleted mountWorkInProgressOffscreenFiber. The prop type of createFiberFromOffscreen is now specified as OffscreenProps, not any. Therefore, I thought mountWorkInProgressOffscreenFiber w...
github.com
다음 글에서 만나요~
'개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Suspense, 더 나아가서 (0) | 2025.04.02 |
|---|
